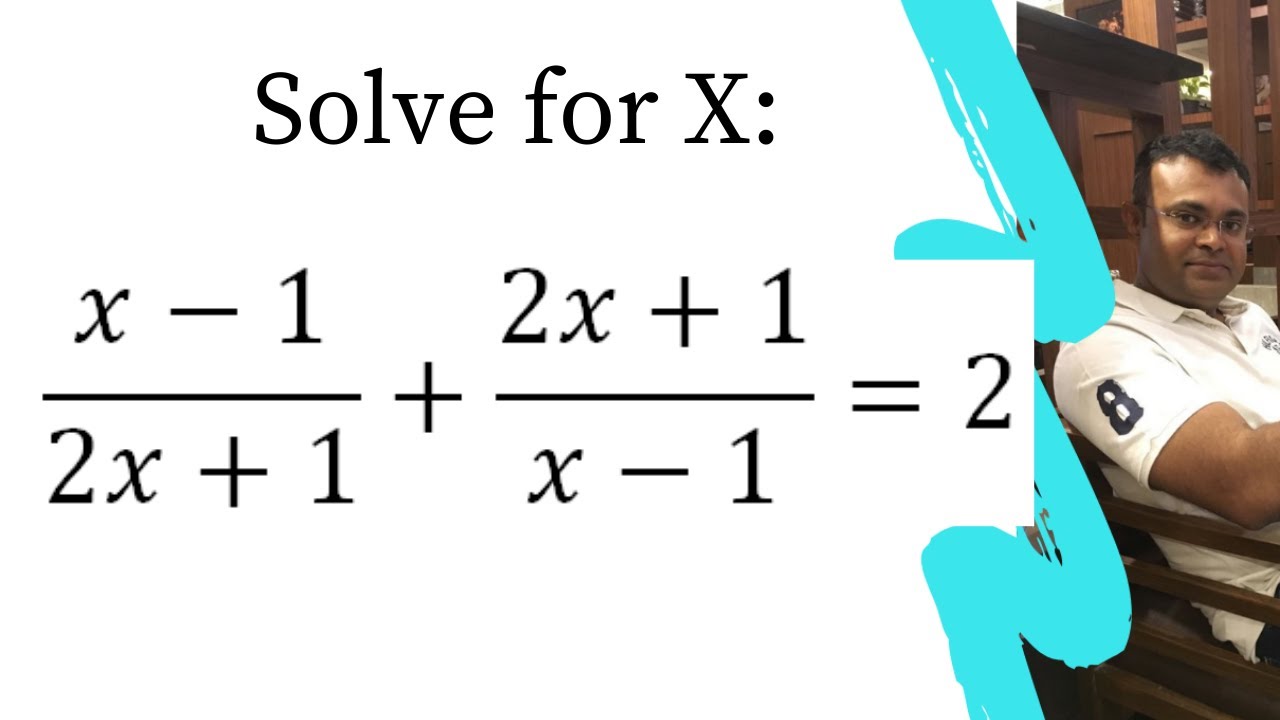Differentiate the function with respect to x: (2x - 1)/(x^2 + 1) - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community

Disequazione: \frac{{{x}+{\left|{x}-{1}\right|}+{3}-{2}{\left({x }-{3}\right)}}}{{{\left|{x}\right|}-{\left|{x}^{2}-{1}\right|}}}\ge{0}

Equazioni 1°, 2°, parametriche, di grado superiore: {\left|{2}{x}-{1 }\right|}={\left|{x}+{1}\right|}+{\left|{x}-{2}\right|}

If left| x right| <1 prove that dfrac { 1-2x }{ 1-x+{ x }^{ 2 } } +dfrac { 2x-{ 4x }^{ 3 } }{ 1-{ x }^{ 2 }+{ x }^{ 4 } } +dfrac { 4{ x }^{ 3 }-8{ x }^{ 7 } }{ 1-{ x }^{ 4 }+{ x }^{ 8 } } +.....infty =dfrac { 1+2x }{ 1+x+{ x }^{ 2 } }

Prove that the equation x^3-2x+1=0 is satisfied by putting x either of the values sqrt{2}sin 45^o, 2sin 18^o, and 2sin 234^o.

Disequazioni: {\left|\frac{{{2}{x}+{5}}}{{{4}{x}-{2}}}-\frac{{{x}-{1}}}{{{1 }-{2}{x}}}\right|}\lt\frac{2}{{3}}




![Solve `[(2x+1)!]/[(x+2)!] xx [(x-1)!]/[(2x-1)!] =3/5` ; `(x in N)` - YouTube Solve `[(2x+1)!]/[(x+2)!] xx [(x-1)!]/[(2x-1)!] =3/5` ; `(x in N)` - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/nyfy6dsU56w/maxresdefault.jpg)